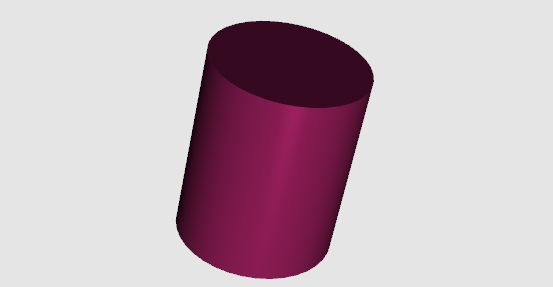
Modern OpenGL绘制圆柱体
本文主要介绍如何使用 C++ 生成圆柱几何体以及如何在 OpenGL 中绘制它。
1.绘制方法
由于我们无法绘制一个完美的圆形底面和圆柱体的弯曲侧面,我们只能通过将底面除以扇区(切片)来采样有限数量的点。因此,它在技术上是通过将这些采样点连接在一起来构建棱柱体。随着样本数量的增加,几何形状更接近于圆柱体。

假设一个圆柱体以原点为中心,半径为r,高度为h。圆柱体上的任意点 ( x, y, z ) 可以从具有相应扇形角θ的圆方程计算出来:

扇形角的范围是从 0 到 360 度。每个步骤的扇形角可以通过以下方式计算:

2.创建存放顶点向量和法向量的结构体:
struct TVertex {
// position
glm::vec3 Position;
// normal
glm::vec3 Normal;
};
3.计算圆周上的点
const int sectorCount = 36;
const float pierRadius = 2.0f;
const float pierHeight = 5.0f;
// 圆周顶点
std::vector<TVertex> getUnitCircleVertices()
{
const float PI = 3.1415926f;
float sectorStep = 2 * PI / sectorCount;
float sectorAngle = 0.0f;
glm::vec3 position;
glm::vec3 normal;
TVertex tVertex;
std::vector<TVertex> unitCircleVertices;
for (int i = 0; i <= sectorCount; ++i)
{
sectorAngle = i * sectorStep;
position.x = pierRadius * cos(sectorAngle);
position.y = 0.0f;
position.z = pierRadius * sin(sectorAngle);
normal.x = cos(sectorAngle);
normal.y = 0.0f;
normal.z = sin(sectorAngle);
tVertex.Position = position;
tVertex.Normal = normal;
unitCircleVertices.push_back(tVertex);
}
return unitCircleVertices;
}
4.获取圆柱体侧面、顶面、底面的顶点和法向量
// generate vertices for a cylinder
void buildCylinderVertices(std::vector<TVertex>& vertices)
{
std::vector<TVertex> unitVertices = getUnitCircleVertices();
// 获取上、下圆周点数组
std::vector<TVertex> vctTop;
std::vector<TVertex> vctBot;
TVertex tVertex;
for(int i = 0; i < unitVertices.size(); ++i)
{
tVertex.Position = unitVertices[i].Position;
tVertex.Position.y = pierHeight;
tVertex.Normal = unitVertices[i].Normal;
vctTop.push_back(tVertex);
tVertex.Position.y = 0.0f;
vctBot.push_back(tVertex);
}
assert(vctTop.size() >= 2);
assert(vctBot.size() >= 2);
// 圆柱侧面
for(int i = 0; i < vctTop.size() - 1; ++i)
{
// 左三角形
vertices.push_back(vctTop[i]);
vertices.push_back(vctBot[i]);
vertices.push_back(vctBot[i+1]);
// 右三角形
vertices.push_back(vctTop[i]);
vertices.push_back(vctTop[i+1]);
vertices.push_back(vctBot[i+1]);
}
// 顶部圆形
glm::vec3 position;
for (int i = 0; i < vctTop.size() - 1; ++i)
{
glm::vec3 position(0.0f, pierHeight, 0.0f);
glm::vec3 normal(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
tVertex.Position = position;
tVertex.Normal = normal;
vertices.push_back(tVertex);
tVertex.Position = vctTop[i].Position;
vertices.push_back(tVertex);
tVertex.Position = vctTop[i+1].Position;
vertices.push_back(tVertex);
}
// 底部圆形
for (int i = 0; i < vctBot.size() - 1; ++i)
{
glm::vec3 position(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glm::vec3 normal(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f);
tVertex.Position = position;
tVertex.Normal = normal;
vertices.push_back(tVertex);
tVertex.Position = vctBot[i].Position;
vertices.push_back(tVertex);
tVertex.Position = vctBot[i+1].Position;
vertices.push_back(tVertex);
}
}
5.将顶点和法向量存入缓冲区
std::vector<TVertex> pierVertices; buildCylinderVertices(pierVertices); unsigned int pierVBO, pierVAO; glGenVertexArrays(1, &pierVAO); glGenBuffers(1, &pierVBO); glBindVertexArray(pierVAO); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, pierVBO); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, pierVertices.size() * sizeof(TVertex), &pierVertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); // position attribute glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(TVertex), (void*)0); // normal attribute glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(TVertex), (void*)offsetof(TVertex, Normal)); glBindVertexArray(0);
6.绘制圆柱体
glClearColor(0.9f, 0.9f, 0.9f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// be sure to activate shader when setting uniforms/drawing objects
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setVec3("lightDirection", -direction); // 平行光方向
//lightingShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);
lightingShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setVec3("viewPos", camera.Position);
// 正交平行的视景体
float fRatio = (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT;
float fHeight = 10.0f;
float fWidth = fHeight*fRatio;
//glm::mat4 projection = glm::ortho(-fWidth, fWidth, -fHeight, fHeight, -10.f, 100.f);
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f); // 透视投影
lightingShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
glm::mat4 viewOrigin = camera.GetViewMatrix();
lightingShader.setMat4("view", viewOrigin);
// 绘制圆柱体
viewOrigin = glm::rotate(viewOrigin, glm::radians(30.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
viewOrigin = glm::rotate(viewOrigin, glm::radians(15.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f));
lightingShader.setMat4("view", viewOrigin);
glm::mat4 modelPier = glm::mat4(1.0f);
lightingShader.setMat4("model", modelPier);
lightingShader.setVec3("objectColor", glm::vec3(0.5f, 0.1f,0.3f));
glBindVertexArray(pierVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, pierVertices.size());
7.删除缓冲区
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &pierVAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &pierVBO);
8.效果

9.完整的项目源代码
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cEUuAmY3JNUbt7sTNvTuyA
提取码:lf5q

2 thoughts on “Modern OpenGL绘制圆柱体”
棒棒哒